GMAT
GMAT
GMAT Integrated Reasoning Overview
What is the Integrated Reasoning Section?
Taking the GMAT? Here’s what the new Integrated Reasoning section is all about.
The Integrated Reasoning Section is unlike other sections found on standardized exams. Strong math and verbal skills will help with this section, but integrated reasoning requires more than a solitary focus of math and English.
We live in a technologically advanced world where decisive and accurate interpretation of data is essential. Recognizing the importance of quantifying the organizational skills necessary for the many challenges of today’s businesses, integrated reasoning reflects real-life situational problems that examine your ability to evaluate and respond to multiple sources of information under time constraints.
What skills are necessary for the Integrated Reasoning Section?
Your experience in multi-tasking, decision-making and maneuvering data in spreadsheets can be an advantage. While formal training in business technology or computer skills is not necessary to perform well, you will be required to make sound analytical decisions and be able to extrapolate and assimilate data that is presented in short reading passages, statements, graphs, spreadsheets, and tables.
It is important to check with individual graduate programs about integrated reasoning’s weighted value of importance in the application process. Although the Quantitative and Verbal scores carry the greatest importance on the GMAT, many business schools will use the Integrated Reasoning section as an additional evaluation point in the overall application criteria.
Study Material
1. In the near future, look for CliffsNotes GMAT with CD-ROM study guide (ISBN #978-1118077528) to be released in the fall of 2012. This newly updated study guide reflects significant content changes with critical information about the new integrated reasoning question types, and explains what to expect in understanding the “thinking processes” required of each exam subject area. Written by the faculty of BTPS Testing, CliffsNotes GMAT contains a diagnostic test, evaluates the exam content format, and prepares you by utilizing four complete model tests (with answers and complete explanations). This up-to-date study guide is provided to all students registered in BTPS Testing workshops offered through the California State Universities.
2. The Official Guide for the GMAT (13th edition) includes stimulated practice problems for the new integrated reasoning section.
3. BTPS Testing administers GMAT preparation workshops through the California State Universities. All workshops include an online integrated reasoning practice test. Click here to view sample integrated reasoning practice problems.
Key Features of Integrated Reasoning
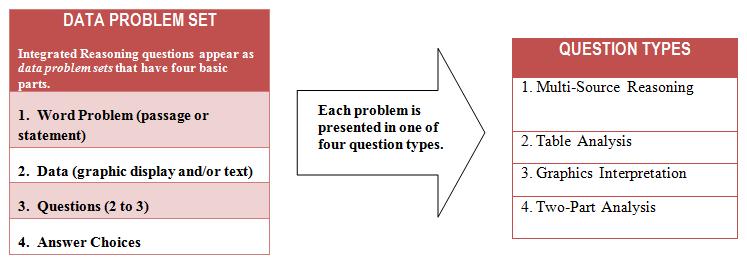
- Questions consist of 12 data problem sets (from 2 to 4 questions in each data problem set).
- Multiple “parts” of each problem set must be completed correctly to receive credit. No partial credit is given.
- As you work, consider each problem set holistically and strategize to solve each one of its components.
- Do not skip questions and answer all parts. Otherwise score results will show an “incorrect” answer. Always take an educated guess.
- You have 30 minutes to complete this section, or approximately 2 ½ minutes per “problem set” to answer all of its parts.
- IR questions have an on-screen calculator available, but the calculator is NOT available for the math questions in the Quantitative Section.
- The IR section is NOT computer-adaptive (like the verbal and quantitative sections).
- Similar to the rest of the GMAT, students cannot move backwards to review previous questions.
- The score range is from 1 to 8, scored separately (like Analytical Writing).
- Some “experimental” IR questions appear on the GMAT to gauge their appropriateness for future tests.
- Just like the Analytical Writing section, IR scores are NOT available on the day of the test. Official scores are mailed separately.
Integrated Reasoning Question Types